Understanding Credit Transfer in E-Waste Management
Effective e-waste management is one of the most important responsibilities for producers, recyclers, and refurbishers under India’s E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022. As Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations continue to evolve, credit transfer has become a critical mechanism to help producers meet their annual recycling obligations efficiently and transparently.
What is Credit Transfer in E-Waste Management?
Under the EPR framework, every registered producer must meet a certain percentage of recycling targets based on the total quantity of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) they place in the market.
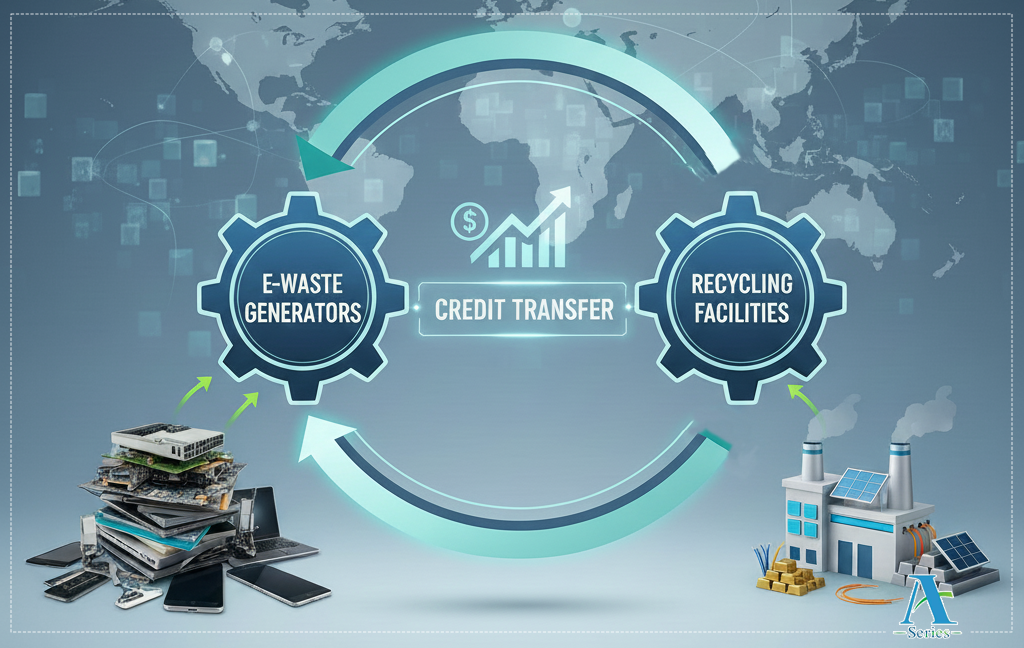
Credit Transfer is a process where:
- Authorized recyclers generate EPR Recycling Certificates after processing e-waste.
- These certificates (credits) can be sold or transferred to producers.
- Producers purchase these credits to fulfill their mandatory EPR recycling targets for a given year.
In simple terms, credit transfer enables producers to comply with EPR targets by acquiring verified recycling credits generated by certified recyclers.
Why is Credit Transfer Important?
Credit transfer offers several benefits across the e-waste ecosystem:
- Ensures Compliance for Producers
Not all producers have the infrastructure or partnerships to collect and recycle e-waste themselves. Credit transfer allows them to meet obligations without operational challenges.
- Encourages More Recycling
Recyclers get additional revenue by selling credits, motivating them to collect and recycle more e-waste formally.
- Increases Transparency
All credits are generated and transferred through the CPCB’s online EPR portal with timestamped records, ensuring traceability and accountability.
- Reduces Illegal or Informal Handling
By creating a financial incentive for formal recycling, credit transfer lowers dependence on informal and unsafe processing.
- Supports Circular Economy Goals
Credit transfer helps channel more e-waste into authorized recyclers, increasing resource recovery and reducing environmental impact.
How Does Credit Transfer Work?
The entire process follows a digital, traceable workflow:
Step 1: Generation of EPR Certificates
Authorized recyclers process eligible e-waste and upload details on the CPCB EPR portal.
After verification, the portal issues EPR Recycling Certificates in kilograms or tonnes.
Step 2: Availability of Credits
These certificates appear in the recycler’s account as available credits for sale or transfer.
Step 3: Producers Request Credits
Producers who need to meet their EPR target request credits from recyclers or PROs (Producer Responsibility Organizations).
Step 4: Transfer Through Portal
Recyclers transfer the credit through the portal, and once approved, it reflects in the producer’s account.
Step 5: Target Fulfillment
Producers can use the credits to meet their annual obligations. If they fall short, penalties and environmental compensation may apply.
Rules Governing Credit Transfer
According to the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022 & subsequent amendments:
- Credit transfer can only be done between authorized recyclers and registered producers.
- The credits must match the specific categories of EEE defined under Schedule I.
- Credits are valid for the financial year in which they are generated.
- Double counting or reuse of credits is strictly prohibited.
- Any manipulation or improper transfer attracts penalties under Environmental Compensation (EC).
Challenges in Credit Transfer
While effective, the credit mechanism has a few challenges:
- Mismatch in demand and supply of credits
- Price fluctuations due to market forces
- Portal delays in verification
- Compliance errors in documentation or processing
- High dependency on recyclers
Producers often rely on consultants to manage compliance and ensure accuracy in the recycling and credit purchase process.
How Can Consultants Help with Credit Transfer?
As consultants specializing in EPR compliance, we assist with:
- Assessing your annual EPR targets
- Identifying reliable, authorized recyclers
- Negotiating and securing cost-effective credits
- Managing all portal formalities on CPCB
- Ensuring documentation accuracy
- Keeping your business fully compliant and audit-ready
This ensures smooth credit transfer without administrative or operational burdens.
Conclusion
Credit transfer is a crucial component of India’s modern e-waste management system. It strengthens the recycling ecosystem, supports circular economy principles, and helps producers stay compliant without operational constraints. With increasing regulatory scrutiny, understanding credit transfer and handling it correctly has never been more important.
If you are a producer, recycler, distributor, or importer seeking support in EPR compliance or credit management, we can help simplify the entire process for you.
Aseries Envirotek India Private Limited provides end-to-end EPR compliance support including credit management, recycler coordination, documentation, portal operations, and audit preparedness.






